Medallion Architecture: A Strategic Framework for Modern Data Management
Organize your data into actionable insights: Medallion Architecture explained.
Navigating the Complexity of Modern Data Ecosystems
As organizations become increasingly data-driven, understanding how to structure and manage data effectively has never been more critical. With a plethora of tools and frameworks, choosing the right approach can feel overwhelming. One approach gaining traction is the Medallion Architecture, a framework designed to bring order, trust, and scalability to your data landscape.
Before diving into Medallion Architecture, here are some foundational concepts:
- Data Lake — A centralized repository for raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data at scale. Highly flexible and cost-effective.
- Data Warehouse — A structured database optimized for querying and reporting, with relational schemas for BI and analytics.
- Delta Lake — A layer that adds transactionality, version control, and data quality to a Data Lake while retaining its flexibility.
- Lambda Architecture — Processes data through two parallel paths: batch layer for historical data and speed layer for real-time. Effective but complex to implement and maintain.
- Kappa Architecture — A single stream processing path for both real-time and historical data. Effective for streaming-first use cases; may be overkill for batch workloads.
What Is Medallion Architecture?
Medallion Architecture is a framework that organizes data into three distinct layers (Bronze, Silver, and Gold), each representing a level of data refinement. Its goal is to streamline governance, improve data quality, and support diverse analytics needs.
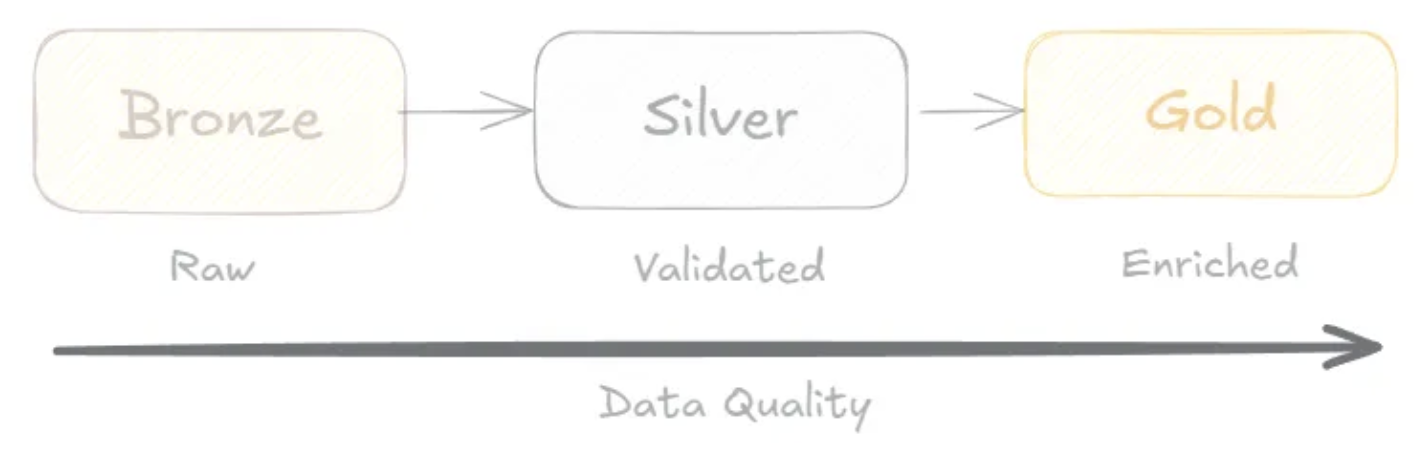
1. Bronze Layer: Raw Data
The starting point where raw, unprocessed data is ingested from various sources. It preserves data in its original format for auditing or reprocessing needs.
2. Silver Layer: Cleaned and Structured Data
The intermediate stage where data is cleaned, normalized, and structured. Its purpose is to standardize and enhance data quality, preparing it for analytical exploration.
3. Gold Layer: Business-Ready Data
Data that is fully refined, aggregated, and optimized for specific business use cases. It is designed to provide actionable insights directly to dashboards, reports, or machine learning models.
Why Choose Medallion Architecture?
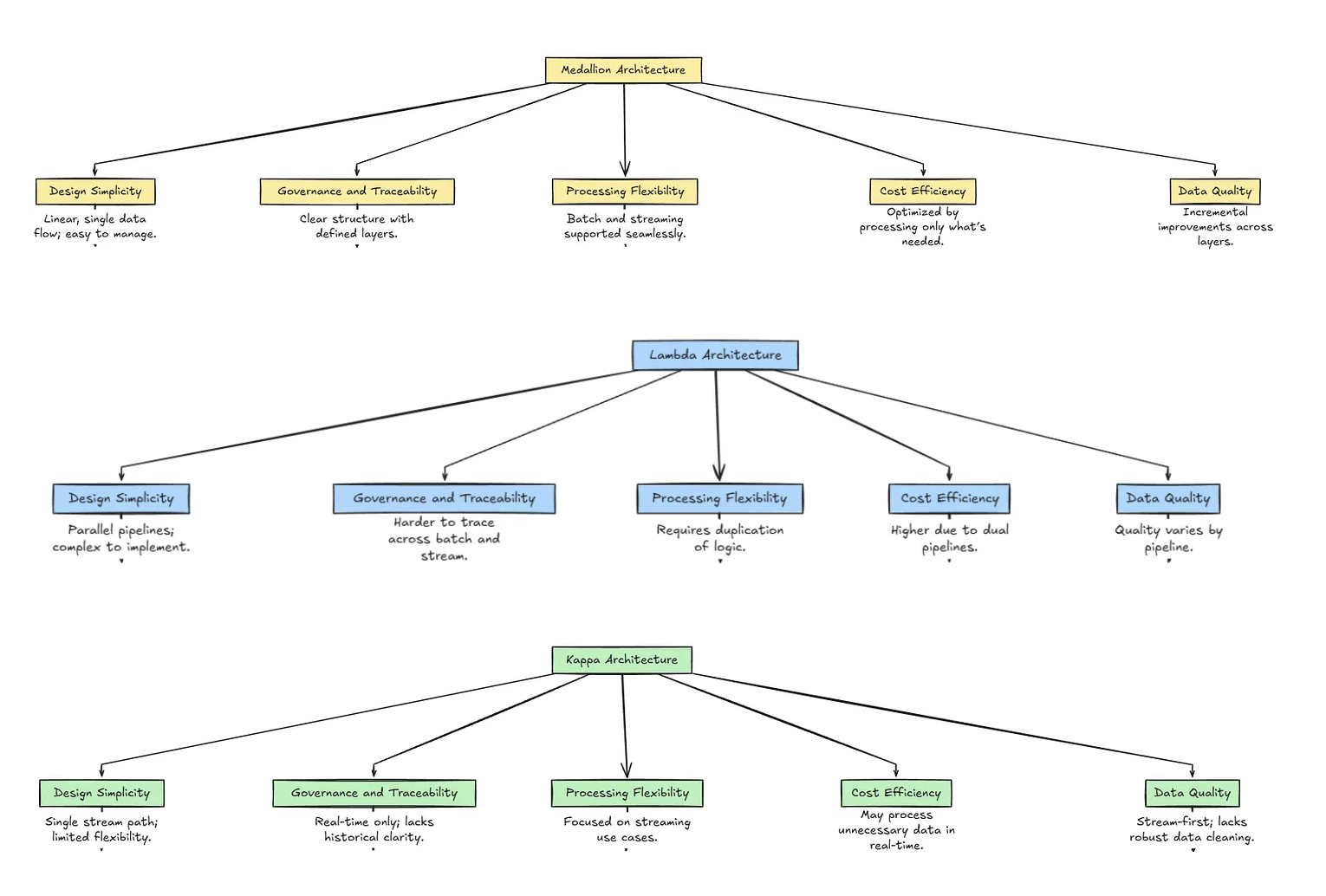
Comparison with Lambda and Kappa Architectures
Medallion Architecture offers a balanced approach by organizing data into layers (Bronze, Silver, Gold) that support both batch and streaming needs with clear governance and incremental refinement. Lambda Architecture requires maintaining dual pipelines (batch and real-time), increasing complexity and risk of inconsistencies. Kappa Architecture simplifies to a single stream processing path but sacrifices flexibility for historical batch reprocessing—making Medallion a versatile option for organizations needing structure, scalability, and adaptability.
Benefits for Business Users
- Trustworthy Insights — Business stakeholders can rely on Gold Layer data for accurate and consistent reporting.
- Streamlined Collaboration — Data is clearly defined at each stage, reducing miscommunication between technical teams and business units.
- Agility — Teams can respond faster to new requirements by leveraging the Bronze Layer for raw data or Silver Layer for exploratory analysis.
Medallion Architecture Is Platform-Agnostic
While Medallion Architecture gained popularity through Databricks, its principles can be applied to other technologies. The key is understanding that Medallion is a framework, not a tool.
Technologies that support Medallion Architecture:
- Cloud platforms: Snowflake, AWS Redshift, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse.
- Traditional databases: PostgreSQL, SQL Server, MySQL (for smaller-scale implementations).
No matter your current stack, Medallion's layered approach can be adapted to fit your infrastructure.
Conclusions
- Medallion Architecture bridges flexibility and governance — It offers the simplicity of a structured framework while maintaining flexibility for diverse analytics needs.
- It is not bound to specific technologies — While Databricks popularized it, Medallion can be implemented on Snowflake, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and many other platforms.
- It drives trust and collaboration — By organizing data into Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers, Medallion enables teams to collaborate efficiently and empowers business users with trustworthy, actionable insights.
- A long-term strategy — This architecture not only meets today's data challenges but also prepares your organization for future scaling and compliance requirements.
Need help designing your data architecture? Contact us at team@simov.io.